Qwen3 represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence, delivering improved reasoning capabilities, multilingual support, and enhanced performance across various benchmarks. This latest addition to the Qwen family of large language models introduces innovative features and architectural improvements that position it as a competitive alternative to leading models from major AI labs. The following comprehensive analysis explores Qwen3's capabilities, technical specifications, and practical applications.
Introduction to Qwen3
Qwen3, released by Alibaba Group in April 2025, marks the newest generation in the Qwen family of large language models. The flagship model, Qwen3-235B-A22B, demonstrates competitive performance against industry leaders such as DeepSeek-R1, o1, o3-mini, Grok-3, and Gemini-2.5-Pro across various benchmarks, including coding, mathematics, and general capabilities. The smaller MoE (Mixture-of-Experts) model, Qwen3-30B-A3B, outperforms QwQ-32B despite using only one-tenth of the activated parameters, while even the compact Qwen3-4B model rivals the capabilities of the significantly larger Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct.
This release includes both MoE and dense models, all available under open-weight licenses. The two MoE models-Qwen3-235B-A22B and Qwen3-30B-A3B-are complemented by six dense models: Qwen3-32B, Qwen3-14B, Qwen3-8B, Qwen3-4B, Qwen3-1.7B, and Qwen3-0.6B, all licensed under Apache 2.0.
The Qwen3 Model Family
MoE Models
- Qwen3-235B-A22B: The flagship model featuring 235 billion total parameters with 22 billion activated parameters. It consists of 94 layers, 64 query attention heads, 4 key-value attention heads, and 128 experts with 8 activated. The model supports a native context length of 32,768 tokens, expandable to 131,072 tokens with YaRN technology.
- Qwen3-30B-A3B: A smaller MoE model with 30.5 billion total parameters and 3.3 billion activated parameters. It has 48 layers, 32 query attention heads, 4 key-value attention heads, and also features 128 experts with 8 activated. Like its larger counterpart, it supports extensive context lengths.
Dense Models
Qwen3 also offers six dense models of varying sizes:
| Model | Layers | Heads (Q / KV) | Context Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-0.6B | 28 | 16 / 8 | 32K |
| Qwen3-1.7B | 28 | 16 / 8 | 32K |
| Qwen3-4B | 36 | 32 / 8 | 32K |
| Qwen3-8B | 36 | 32 / 8 | 128K |
| Qwen3-14B | 40 | 40 / 8 | 128K |
| Qwen3-32B | 64 | 64 / 8 | 128K |
These models are designed to accommodate different computational requirements and use cases, from resource-constrained environments to high-performance applications.
Key Innovations and Features
Hybrid Thinking Modes
One of Qwen3's most distinctive features is its support for dual thinking modes within a single model architecture:
- Thinking Mode: Designed for complex tasks requiring logical reasoning, mathematical computation, or coding challenges. In this mode, the model takes time to reason step by step before delivering an answer, similar to how humans approach complex problems.
- Non-Thinking Mode: Optimized for providing quick responses to more straightforward queries, maintaining efficiency for general-purpose dialogue.
This innovative approach allows users to control the model's reasoning depth based on task complexity. For challenging problems, the thinking mode enables extended reasoning, while simpler questions can be addressed directly without unnecessary computational overhead. The implementation includes a soft switching mechanism, enabling users to dynamically control behavior by adding /think and /no_think tags to prompts or system messages.
Expansive Multilingual Capabilities
Qwen3 supports an impressive 119 languages and dialects, tripling the coverage of its predecessor, Qwen2.5. This extensive linguistic range spans multiple language families:
- Indo-European (English, French, Spanish, Russian, Hindi, etc.)
- Sino-Tibetan (Chinese variants, Burmese)
- Afro-Asiatic (Arabic variants, Hebrew)
- Austronesian (Indonesian, Malay, Tagalog)
- Dravidian (Tamil, Telugu, Kannada)
- Turkic (Turkish, Uzbek)
- Tai-Kadai, Uralic, Austroasiatic, and others
This comprehensive multilingual support positions Qwen3 for global adoption, particularly in regions with linguistic diversity.
Advanced Agentic Capabilities
Qwen3 has been optimized for coding and agentic operations, with enhanced support for Model-Conditional Prompting (MCP). These improvements enable more sophisticated applications, such as autonomous agents and precise developer tooling. The models excel at tool integration in both thinking and non-thinking modes, achieving leading performance among open-source models in complex agent-based tasks.
Technical Architecture and Training
Pre-training Process
The pre-training dataset for Qwen3 is substantially larger than its predecessor's, comprising approximately 36 trillion tokens covering 119 languages and dialects-nearly twice the 18 trillion tokens used for Qwen2.5. The data collection process was rigorous:
- Web-sourced content was supplemented with text extracted from PDF-like documents
- Qwen2.5-VL was employed to extract text from documents
- Qwen2.5 was used to enhance the quality of extracted content
- Qwen2.5-Math and Qwen2.5-Coder generated synthetic data to augment math and code content
The pre-training followed a three-stage process:
- Stage 1 (S1): Training on over 30 trillion tokens with a context length of 4K tokens, establishing foundational language skills and general knowledge
- Stage 2 (S2): Training on an additional 5 trillion tokens with an increased proportion of knowledge-intensive data (STEM, coding, reasoning)
- Stage 3 (S3): Extension of context length to 32K tokens using high-quality long-context data
This extensive training regime has resulted in Qwen3 dense base models matching or exceeding the performance of larger Qwen2.5 models. For example, Qwen3-1.7B/4B/8B/14B/32B-Base perform comparably to Qwen2.5-3B/7B/14B/32B/72B-Base, respectively, while excelling in specialized domains like STEM, coding, and reasoning.
Post-training Methodology
To develop the hybrid model capable of both detailed reasoning and rapid responses, a four-stage training pipeline was implemented:
- Long chain-of-thought (CoT) cold start: Fine-tuning on diverse CoT data spanning mathematics, coding, logical reasoning, and STEM problems
- Reasoning-based reinforcement learning (RL): Scaling computational resources for RL with rule-based rewards to enhance exploration and exploitation
- Thinking mode fusion: Integration of non-thinking capabilities into the thinking model through fine-tuning on combined data
- General RL: Application of reinforcement learning across more than 20 general-domain tasks to strengthen capabilities and correct undesired behaviors
Performance and Benchmark Results
According to benchmark evaluations, Qwen3 models demonstrate impressive performance across various metrics:

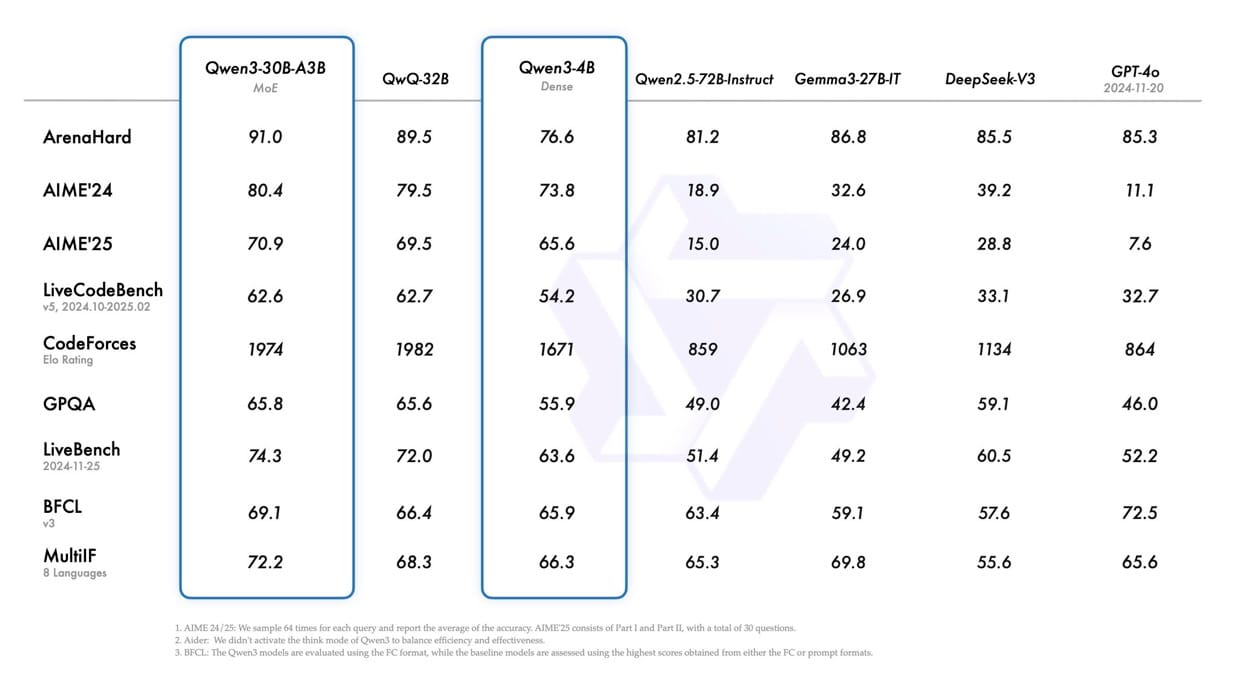
These benchmarks indicate that Qwen3 models are competitive with or surpass industry-leading alternatives in several key areas. The flagship Qwen3-235B-A22B model consistently ranks among the top performers, particularly in challenging reasoning tasks.
When comparing the older Qwen models with competitors, there are noticeable improvements in benchmark performance. Qwen3-30B-A3B significantly outperforms Qwen-30B-A3B (shown as Qwen3-30B-A3B in the image), and even the smaller Qwen3 models demonstrate enhanced capabilities compared to their predecessors.
Development and Practical Applications
Using Qwen3 Models
Qwen3 models are accessible through multiple platforms, including Hugging Face, ModelScope, and Kaggle. For deployment, SGLang and vLLM are recommended frameworks, while local usage is supported through tools such as Ollama, LMStudio, MLX, llama.cpp, and KTransformers.
A basic example of using Qwen3-30B-A3B with Hugging Face transformers:
from modelscope import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B"
# Load the tokenizer and model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# Prepare model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True # Toggle between thinking and non-thinking modes
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Generate text
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=32768
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
# Parse thinking content
try:
# Find </think> token (151668)
index = len(output_ids) - output_ids[::-1].index(151668)
except ValueError:
index = 0
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print("thinking content:", thinking_content)
print("content:", content)
For deployment using SGLang (version 0.4.6.post1 or later) to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint:
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B --reasoning-parser qwen3
For deployment using vLLM (version 0.8.4 or later):
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B --enable-reasoning --reasoning-parser deepseek_r1
For local development using Ollama:
ollama run qwen3:30b-a3b
Agentic Capabilities
Qwen3 excels in tool-calling capabilities and is compatible with Qwen-Agent, which encapsulates tool-calling templates and parsers to simplify implementation. An example of agent implementation:
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# Define LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'Qwen3-30B-A3B',
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
}
# Define Tools
tools = [
{'mcpServers': { # MCP configuration
'time': {
'command': 'uvx',
'args': ['mcp-server-time', '--local-timezone=Asia/Shanghai']
},
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}},
'code_interpreter', # Built-in tools
]
# Create Agent
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, function_list=tools)
# Generate responses
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/ Introduce the latest developments of Qwen'}]
for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
pass
print(responses)
This flexibility in implementation enables diverse applications across various domains, from conversational agents to specialized tools for specific professional contexts.
Future Development Directions
Qwen3 represents a significant milestone in the journey toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). Looking ahead, the development team aims to enhance models across multiple dimensions:
- Refining model architectures and training methodologies
- Scaling data and increasing model size
- Extending context length capabilities
- Broadening modality support
- Advancing reinforcement learning with environmental feedback for long-horizon reasoning
The team envisions a transition from an era focused on training models to one centered on training agents. Future iterations are expected to bring meaningful advancements to both professional and personal applications.
Conclusion
Qwen3 represents a significant advancement in large language model technology, offering competitive performance against industry leaders while providing unique capabilities like hybrid thinking modes and extensive multilingual support. The open-weighted approach, with models ranging from compact 0.6B parameter versions to the powerful 235B-A22B flagship, makes advanced AI accessible across various computational environments and use cases.
The model's architectural innovations-particularly its mixture-of-experts design and ability to dynamically switch between thinking and non-thinking modes-provide both efficiency and flexibility for diverse applications. As AI continues to evolve toward more sophisticated reasoning and agency, Qwen3 stands as an important contribution to the field, balancing performance, accessibility, and practical utility.
With its strong performance on key benchmarks and comprehensive development ecosystem, Qwen3 offers researchers, developers, and organizations powerful tools to build innovative AI solutions. The ongoing commitment to enhancing capabilities across multiple dimensions suggests that future iterations will continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in artificial intelligence.






